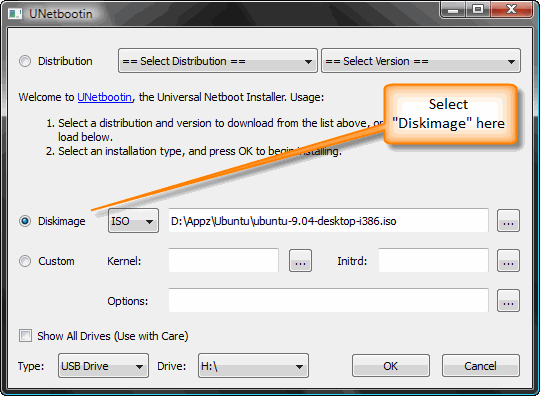
Critical thinking involves determining the meaning and significance of what is observed or expressed, or, concerning a given inference or argument
Electronic commerce, commonly known as (electronic marketing) e-commerce or eCommerce, consists of the buying and selling of products or services
keyless entry system allows u to unlock and lock the computer with out touching the computer
online learning get tutoring online
telecommuting employment at home while communicating with the workplace by phone or fax or modem
Browser hijacking is the modification of a web browser's settings by malware
hacking a hacker is a person who breaks into computers, usually by gaining access to administrative controls
A hard ware firewall is built into a router or a stand -alone device
Thursday, December 23, 2010
Tuesday, December 21, 2010
Indexes: a system used to make finding information easier.
Keywords: the words that are used to reveal the internal structure of an author's reasoning.
Libel: defamation by written or printed words, pictures, or in any form other than by spoken words or gestures
Link List: contains a null reference
Math Symbols: a listing of common symbols found within all branches of mathematics
News Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Peer-to-Peer: computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or work loads between peers.
Phrase Searching: is used to search for words as phrases.
Plagiarism: is defined in dictionaries as "the wrongful appropriation, close imitation, or purloining and publication, of another author's language
Podcatcher: a computer program used to download various media via an RSS or XML feed.
Keywords: the words that are used to reveal the internal structure of an author's reasoning.
Libel: defamation by written or printed words, pictures, or in any form other than by spoken words or gestures
Link List: contains a null reference
Math Symbols: a listing of common symbols found within all branches of mathematics
News Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Peer-to-Peer: computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or work loads between peers.
Phrase Searching: is used to search for words as phrases.
Plagiarism: is defined in dictionaries as "the wrongful appropriation, close imitation, or purloining and publication, of another author's language
Podcatcher: a computer program used to download various media via an RSS or XML feed.
Public Domain: comprises copyright-free works: anyone can use them in any way and for any purpose. Proper attribution to the author
Related Search: software program that searches a database and gathers and reports information that contains or is related to specified terms.
Search Engine: is designed to search for information on the World Wide Web and FTP servers.
Shared bookmark: a method for Internet users to organize, store, manage and search for bookmarks of resources online.
Trademark: a distinctive sign or indicator used by an individual, business organization, or other legal entity
Wiki: a website that allows the easy creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text
Wildcard character: a special character that represents one or more other characters
Business-to-Business: describes commerce transactions between businesses, such as between a manufacturer and a wholesaler, or between a wholesaler and a retailer.
Business-to-consumer: describes activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and/or services.
Business-to-government: a derivative of B2B marketing and often referred to as a market definition of "public sector marketing" which encompasses marketing products
Related Search: software program that searches a database and gathers and reports information that contains or is related to specified terms.
Search Engine: is designed to search for information on the World Wide Web and FTP servers.
Shared bookmark: a method for Internet users to organize, store, manage and search for bookmarks of resources online.
Trademark: a distinctive sign or indicator used by an individual, business organization, or other legal entity
Wiki: a website that allows the easy creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text
Wildcard character: a special character that represents one or more other characters
Business-to-Business: describes commerce transactions between businesses, such as between a manufacturer and a wholesaler, or between a wholesaler and a retailer.
Business-to-consumer: describes activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and/or services.
Business-to-government: a derivative of B2B marketing and often referred to as a market definition of "public sector marketing" which encompasses marketing products
Indexes: a system used to make finding information easier.
Keywords: the words that are used to reveal the internal structure of an author's reasoning.
Libel: defamation by written or printed words, pictures, or in any form other than by spoken words or gestures
Link List: contains a null reference
Math Symbols: a listing of common symbols found within all branches of mathematics
News Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Peer-to-Peer: computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or work loads between peers.
Phrase Searching: is used to search for words as phrases.
Plagiarism: is defined in dictionaries as "the wrongful appropriation, close imitation, or purloining and publication, of another author's language
Podcatcher: a computer program used to download various media via an RSS or XML feed.
Keywords: the words that are used to reveal the internal structure of an author's reasoning.
Libel: defamation by written or printed words, pictures, or in any form other than by spoken words or gestures
Link List: contains a null reference
Math Symbols: a listing of common symbols found within all branches of mathematics
News Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Peer-to-Peer: computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or work loads between peers.
Phrase Searching: is used to search for words as phrases.
Plagiarism: is defined in dictionaries as "the wrongful appropriation, close imitation, or purloining and publication, of another author's language
Podcatcher: a computer program used to download various media via an RSS or XML feed.
Monday, December 20, 2010
Web Cache: the caching of web documents (e.g., HTML pages, images) to reduce bandwidth usage, server load, and perceived lag. A web cache stores copies of documents passing
Website: a collection of related web pages, images, videos or other digital assets that are addressed
Webapp: In earlier types of cloud computing, each application had its own client program which served as its user interface and had to be separately installed on each user
Wiki: is a website that allows the easy creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text
Blog: (a blend of the term web log is a type of website or part of a website. Blogs are usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary
Boolean Logic: a complete system for logical operations, used in many systems. It was named after George Boole, who first defined an algebraic system of logic
Copyright: a set of exclusive rights granted by the law of a jurisdiction to the author or creator of an original work, including the right to copy
Directories: A typical file system may contain thousands (or even hundreds of thousands) of folders.
Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Secure Sockets Layer: Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are cryptographic protocols that "provide communications security over the Internet TLS
Website: a collection of related web pages, images, videos or other digital assets that are addressed
Webapp: In earlier types of cloud computing, each application had its own client program which served as its user interface and had to be separately installed on each user
Wiki: is a website that allows the easy creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text
Blog: (a blend of the term web log is a type of website or part of a website. Blogs are usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary
Boolean Logic: a complete system for logical operations, used in many systems. It was named after George Boole, who first defined an algebraic system of logic
Copyright: a set of exclusive rights granted by the law of a jurisdiction to the author or creator of an original work, including the right to copy
Directories: A typical file system may contain thousands (or even hundreds of thousands) of folders.
Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Secure Sockets Layer: Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are cryptographic protocols that "provide communications security over the Internet TLS
Indexes: a system used to make finding information easier.
Keywords: the words that are used to reveal the internal structure of an author's reasoning.
Libel: defamation by written or printed words, pictures, or in any form other than by spoken words or gestures
Link List: contains a null reference
Math Symbols: a listing of common symbols found within all branches of mathematics
News Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Peer-to-Peer: computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or work loads between peers.
Phrase Searching: is used to search for words as phrases.
Plagiarism: is defined in dictionaries as "the wrongful appropriation, close imitation, or purloining and publication, of another author's language
Podcatcher: a computer program used to download various media via an RSS or XML feed
Keywords: the words that are used to reveal the internal structure of an author's reasoning.
Libel: defamation by written or printed words, pictures, or in any form other than by spoken words or gestures
Link List: contains a null reference
Math Symbols: a listing of common symbols found within all branches of mathematics
News Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Peer-to-Peer: computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or work loads between peers.
Phrase Searching: is used to search for words as phrases.
Plagiarism: is defined in dictionaries as "the wrongful appropriation, close imitation, or purloining and publication, of another author's language
Podcatcher: a computer program used to download various media via an RSS or XML feed
Hypertext Transfer Protocol: a networking protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication
Internet Protocol Address: a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet
Internet Service Provider: a company that offers its customers access to the Internet
Mosaic: the art of creating images with an assemblage of small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials
Podcast: a series of digital media files (either audio or video) that are released episodically and often downloaded through web syndication.
Portal: a general term describing an opening in the walls of a building, gate or fortification, and especially a grand entrance to an important structure
Really Simple Syndication: a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works—such as blog entries, news headlines, audio
Social Networking Site: an online service, platform, or site that focuses on building and reflecting of social networks or social relations among people
Uniform Resource Locator: a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) that specifies where an identified resource is available and the mechanism for retrieving it.
Web 2.0: commonly associated with web applications that facilitate interactive systemic biases, interoperability, user-centered design and developing the World Wide Web.
Internet Protocol Address: a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet
Internet Service Provider: a company that offers its customers access to the Internet
Mosaic: the art of creating images with an assemblage of small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials
Podcast: a series of digital media files (either audio or video) that are released episodically and often downloaded through web syndication.
Portal: a general term describing an opening in the walls of a building, gate or fortification, and especially a grand entrance to an important structure
Really Simple Syndication: a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works—such as blog entries, news headlines, audio
Social Networking Site: an online service, platform, or site that focuses on building and reflecting of social networks or social relations among people
Uniform Resource Locator: a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) that specifies where an identified resource is available and the mechanism for retrieving it.
Web 2.0: commonly associated with web applications that facilitate interactive systemic biases, interoperability, user-centered design and developing the World Wide Web.
ActiveX: a framework for defining reusable software components in a programming language independent way.
Client: is an application or system that accesses a remote service on another computer system, known as a server, by way of a network The term was first applied to devices
Cookie: a web cookie, browser cookie, and HTTP cookie, is a piece of text stored by a user 's web browser
Digital Certificate: a public key certificate (also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate) is an electronic document which uses a digital signature to bind a public key
Domain: an identification label that defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority, or control in the Internet.
File Transfer Protocol: is a standard network protocol used to copy a file from one host to another over a TCP/IP-based network, such as the Internet.
Geographic Imaging: division of the National Geographic Society (NGS) headquartered in Washington, D.C., USA, is a stock photography agency
Hit: a strike (attack), the act of hitting someone or something to cause physical harm.
Home Page: has various related meanings to do with web sites: It most often refers to the initial or main web page of a web site, sometimes called the front page
Hypertext markup Language: is the predominant markup language for web pages
Client: is an application or system that accesses a remote service on another computer system, known as a server, by way of a network The term was first applied to devices
Cookie: a web cookie, browser cookie, and HTTP cookie, is a piece of text stored by a user 's web browser
Digital Certificate: a public key certificate (also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate) is an electronic document which uses a digital signature to bind a public key
Domain: an identification label that defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority, or control in the Internet.
File Transfer Protocol: is a standard network protocol used to copy a file from one host to another over a TCP/IP-based network, such as the Internet.
Geographic Imaging: division of the National Geographic Society (NGS) headquartered in Washington, D.C., USA, is a stock photography agency
Hit: a strike (attack), the act of hitting someone or something to cause physical harm.
Home Page: has various related meanings to do with web sites: It most often refers to the initial or main web page of a web site, sometimes called the front page
Hypertext markup Language: is the predominant markup language for web pages
Web Cache: the caching of web documents (e.g., HTML pages, images) to reduce bandwidth usage, server load, and perceived lag. A web cache stores copies of documents passing
Website: a collection of related web pages, images, videos or other digital assets that are addressed
Webapp: In earlier types of cloud computing, each application had its own client program which served as its user interface and had to be separately installed on each user
Wiki: is a website that allows the easy creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text
Blog: (a blend of the term web log is a type of website or part of a website. Blogs are usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary
Boolean Logic: a complete system for logical operations, used in many systems. It was named after George Boole, who first defined an algebraic system of logic
Copyright: a set of exclusive rights granted by the law of a jurisdiction to the author or creator of an original work, including the right to copy
Directories: A typical file system may contain thousands (or even hundreds of thousands) of folders.
Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Secure Sockets Layer: Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are cryptographic protocols that "provide communications security over the Internet TLS
Website: a collection of related web pages, images, videos or other digital assets that are addressed
Webapp: In earlier types of cloud computing, each application had its own client program which served as its user interface and had to be separately installed on each user
Wiki: is a website that allows the easy creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text
Blog: (a blend of the term web log is a type of website or part of a website. Blogs are usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary
Boolean Logic: a complete system for logical operations, used in many systems. It was named after George Boole, who first defined an algebraic system of logic
Copyright: a set of exclusive rights granted by the law of a jurisdiction to the author or creator of an original work, including the right to copy
Directories: A typical file system may contain thousands (or even hundreds of thousands) of folders.
Feed: a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
Secure Sockets Layer: Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are cryptographic protocols that "provide communications security over the Internet TLS
http
a protocol (utilizing TCP) to transfer hypertext requests and information between servers and browsers


Saturday, December 18, 2010
digital certificate
is an electronic "credit card" that
establishes your credentials when doing business
establishes your credentials when doing business
cookie
information that a Web site puts on your hard disk so that it can
remember something about you at a later time.
remember something about you at a later time.
client
describes the relationship between two computer programs in which
one program, the client, makes a service request from another program
one program, the client, makes a service request from another program
ACTIVE X
is a set of object-oriented programming (OOP) technologies and tools
that Microsoft developed for Internet Explorer
that Microsoft developed for Internet Explorer
worm
is a self-replicating virus that does not alter files but resides in
active memory and duplicates itself.
active memory and duplicates itself.
rdf summary
An XML format used to syndicate news, blog posts, forum threads, and
other content among different web sites
other content among different web sites
pyramid schemes
non-sustainable business model that involves promising
participants payment, services or ideals
participants payment, services or ideals
phishing
is the criminally fraudulent process
of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as usernames
of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as usernames
netiquette
netiquette refers to an established set of rules developed by the community itself, rather than an independent body
logic bomb
a logic bomb, also called slag code, is some code.
inserted surreptitiously or intentionally, that is designed
inserted surreptitiously or intentionally, that is designed
fraud
A false representation of a matter of fact—whether by words or by conduct, by
false or misleading allegations, or by concealment of what should have been
false or misleading allegations, or by concealment of what should have been
filtering
Selective
presentation or deliberate manipulation of information to make it more
acceptable
presentation or deliberate manipulation of information to make it more
acceptable
windows mail
The Windows Mail Junk E-mail and Phishing Filter will be updated automatically
one time per month
one time per month
text messaging
SMS messaging allows for short
text messages to be sent from one cell phone to another

text messages to be sent from one cell phone to another

spam
is flooding the Internet with many copies of the same message, in an
attempt to force the message on people who would not otherwise choose to receive

attempt to force the message on people who would not otherwise choose to receive

maling list
A list of users of the Internet
or another computer network who all receive copies of electronic mail
or another computer network who all receive copies of electronic mail

instant messaging
The transmission of an electronic message over a computer
network using software that immediately displays the message

network using software that immediately displays the message
Thursday, December 16, 2010
Wireless Internet Service Provider
A wireless Internet service provider (WISP) is an Internet service provider (ISP
) that allows subscribers to connect to a server using a wireless connection
) that allows subscribers to connect to a server using a wireless connection
WiMax
is a wireless industry coalition whose members organized to advance IEEE
802.16 standards for broadband wireless access
802.16 standards for broadband wireless access
Server Operating System
A server operating system is software that was especially developed to serve as a platform for running multi-user computer programs, applications that are networked and programs
Router
a router is a device or, in some cases, software in a computer,
that determines the next network point to which a packet should be
that determines the next network point to which a packet should be
Public Switched Telephone Network
is the world's collection
of interconnected voice-oriented public telephone networks,
of interconnected voice-oriented public telephone networks,
Proxy Server
a proxy server is a server a computer system or an
application program that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients
application program that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients
Peer-Peer Network
A network of computers configured to
allow certain files and folders to be shared with everyone or with selected people
allow certain files and folders to be shared with everyone or with selected people
Modem
modem modulates outgoing digital signals from a computer or
other digital device to analog signals for a conventional copper twisted pair
other digital device to analog signals for a conventional copper twisted pair
Local Area Conector
A local area network (LAN) supplies networking capability to a ...
Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) that supports controlled access to LAN
Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) that supports controlled access to LAN
Internet
The Internet, sometimes called simply "the Net," is a worldwide
system of computer networks
system of computer networks
Firewall
A firewall is a set of related programs, located at a network gateway server,
that protects the resources of a private network from users
that protects the resources of a private network from users
Extranet
An extranet is a computer network that allows controlled access from the outside
, for specific business or educational purposes.
, for specific business or educational purposes.
Digital Subscriber Line
technology provides high bandwidth network
connections to homes and small businesses.
connections to homes and small businesses.
Communication Channels
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or
channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire
channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire
Client
Client server describes the relationship between two computer programs in which
one program, the client, makes a service request from another program
one program, the client, makes a service request from another program
Cable Modem
A cable modem is a device that enables you to hook up your PC to a local cable
TV line and receive data at about 1.5 Mbps.
TV line and receive data at about 1.5 Mbps.
Biometric Security Measures
It measures the percent of invalid inputs which are incorrectly accepted
Thursday, December 9, 2010
class work 12/9
why i think the roman empire fell was because there was to much equality
One of the reasons that it fell was the use of violence by the Roman elite.
Another key factor was that Roman republican generals such as Marius ,
Sulla, Pompey and Gaius Julius Caesar had in effect,
private armies that looked to them for retirement packages and to defend their interests
This was all set against the massive expansion of the empire from the Punic wars onward - a growth in both territory and wealth and the dislocations that this caused
Monday, December 6, 2010
monday classwork
Greek Roman
Aphrodite Venus
Ares Mars
Poseidon Neptune
Zeus Jupiter
Kronos Saturn
Hermes Mercury
Hades Pluto
Aphrodite Venus
Ares Mars
Poseidon Neptune
Zeus Jupiter
Kronos Saturn
Hermes Mercury
Hades Pluto
Wednesday, December 1, 2010
queries
They are a request for information from a database and theres are three general methods for posing queries.
program
Its when it shows the programs you have in your computer in the home Button in the bottom left hand corner of your screen.
print queue
Is a disk space that holds output designated for the printer until the printer can receive it
point
To move the cursor onto a line or image on screen by rolling a mouse across the desk or by pressing the arrow keys.
one to many relationship
Is when many relationships is when a row in Table A may have many linked records in Table B but each rows in Table B may have only one connecting row in Table A.
nonprinting characters
Is the display information or the C haracters replaced with a white space while printing.
modern
Is the text keyed to an alphabetical list of works cited that appears at the end of the work.
mixed cell refrence
Is a cell reference that has either the row or column is made absolute, but not both, using the dollar sign.
microsoft visual basic for application
Is a implementation of Microsoft's event-driven programming language
mhtml format
Is a web page archive format used to combine resources that are typically represented by external links.
manual page break
A code inserted in a document that tells to break up a document or text from each other.
manual line break
Is a manual line break ends the current line and continues the text on the next line
manual column break
Is used in a word processing document where there are columns that are seperate to 2 or 3 in a sheet.
line chart
Is a chart that displays information as a series of data points connected by straight line segments.
leader character
Is when seperating 2 text away from each other and the 2nd text is the Leading character
layout
Is the process of placing and arranging and rearranging text and graphics on the page to produce documents.
justified
It is arranged so that each line begins, or ends, right under the other, creating an even, vertical edge to a block of text.
insertion point
Is the point where the next characters typed from the keyboard will appear on the display screen.
information bar
Is the place where displays information about security, downloads, blocked pop-up windows, and other activities.
gridlines
They are the gray lines that divide each of the cells, rows, and columns in a spreadsheet.
graphical user interface
formula bar
Is the contents of the current or active cell, located above the worksheet column headings
find
Is when it searches the computer to locates files, and applies a user-specified action on each matched file.
file placeholders
Is a user field is a special type of field that stores references to QuickBase users.
dialog boxes
Is a small temporary window in a graphical user interface that appears to request information
design view
The view of table, query, form, and macro objects that enables you to create or change an object.
criteria
They are requirements that must be met for an individual to be included in a research study
copy right
Is the set of exclusive rights granted to the author or creator of an original work, including the right to copy, distribute and adapt the work.
control
Is an element of a graphical user interface (GUI) that displays an information arrangement changeable by the user, such as a window or a text box.
Compatibility mode
A feature of a
computer or operating system that enables it to run programs written
computer or operating system that enables it to run programs written
Clustered column chart
columns that are bunched together so that you are not able to read the information thats their
Circular reference
A situation
created by a programming error in which two or more entities each refer to.
created by a programming error in which two or more entities each refer to.
Cell address
A combination of a letter and
a number that specifies the column and row in which a cell is located.
a number that specifies the column and row in which a cell is located.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)